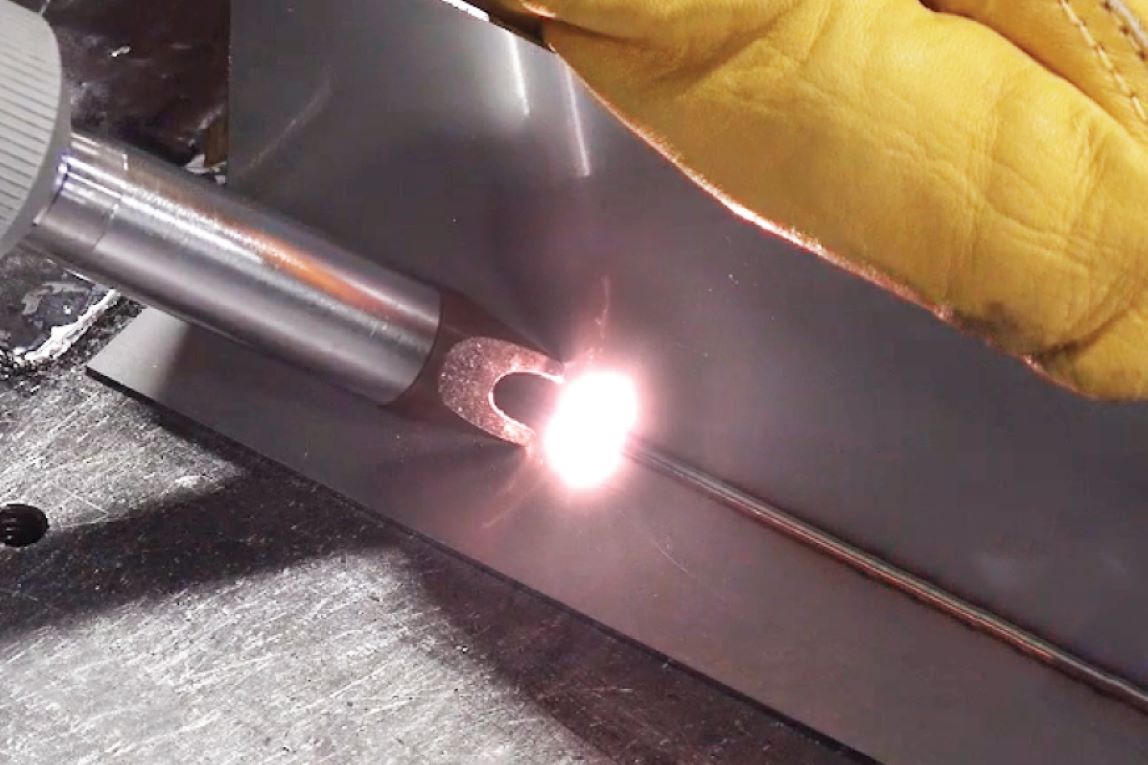
The ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel code (BPVC) is a set of guidelines, regulations, and processes developed and published by the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME). This document, updated once every two years, is intended to define and quantify the requirements for safe fabrication and operation of boilers and pressure vessels.
Updates to Section IX of the ASME BPVC offer some exciting news for laser welding and, most importantly, qualifications for handheld laser welding. This recognition from ASME acknowledges that handheld laser welding devices like LightWELD are fully capable of creating strong and safe welds across a wide variety of joint types and materials. With this update, ASME documents the specific procedures to be used in laser welding of boilers and pressure vessels and the qualification of welders employed in welding such components.
The ASME BPVC encompasses several main criteria which help users to comply with applicable regulations within their jurisdictions while achieving operational, cost, and safety benefits. Section IX of the BPVC codes and standards can be accessed from ASME here.
As with any welding process in the BPVC, handheld laser welding must satisfy a variety of specific acceptance criteria, with examples including shear tests and tensile strength tests. These acceptance criteria ensure that laser welded joints meet the required standards of the code. With this update, handheld laser welding processes have been qualified for a wide variety of boiler and pressure vessel joints.
Compliance with the BPVC also requires that welders are similarly evaluated on their ability to provide high-quality welds that follow outlined procedures. Although weld quality and welder capability are evaluated agnostically from the welding method, a notable quality of handheld laser welding is ease of operation.

The efficiency and ease-of-use offered by handheld laser welding increases productivity and allows even novice welders to quickly and reliably make high-quality welds for both repetitive tasks and complex fabrication projects.
The inclusion of handheld laser welding in the code aligns regulatory standards with industry practices while promoting safety and compliance. ASME codes and standards often influence and are influenced by international standards. Recognition of handheld laser welding indicates confidence in handheld laser welding’s ability to meet or exceed required quality standards, aiding in the widespread acceptance of the technology.
Learn more about handheld laser welding and LightWELD Handheld Laser Welding & Cleaning Systems here.