The terms "ultrafast" and "ultrashort" refers to a class of lasers that emit pulses of light with extremely short pulse durations in the order of picoseconds (10-12 seconds) and femtoseconds (10-15 seconds). To understand just how short ultrafast pulse durations are, one need only reference the speed of light: 300,000 km per second. In a single femtosecond, light travels approximately 0.3 µm. This means that an IPG fiber laser with a 250 femtosecond pulse duration emits a pulse of light that is just 75 µm long.
Despite these remarkable properties, IPG ultrafast fiber lasers are robust and reliable tools for scientific, medical, and industrial materials processing applications. Ultrafast lasers have become increasing popular over the years in a variety of industries for applications that require precise control of pulse duration and extremely high peak powers. IPG laser technology powers ultrafast lasers that are uniquely compact, cost effective, and easy to integrate for precision applications including cutting, drilling, ablating, and structuring a wide range of materials.
- Home
- Technology
- Ultrafast Laser Technology

Ultrafast Lasers
What Are Ultrafast Lasers?
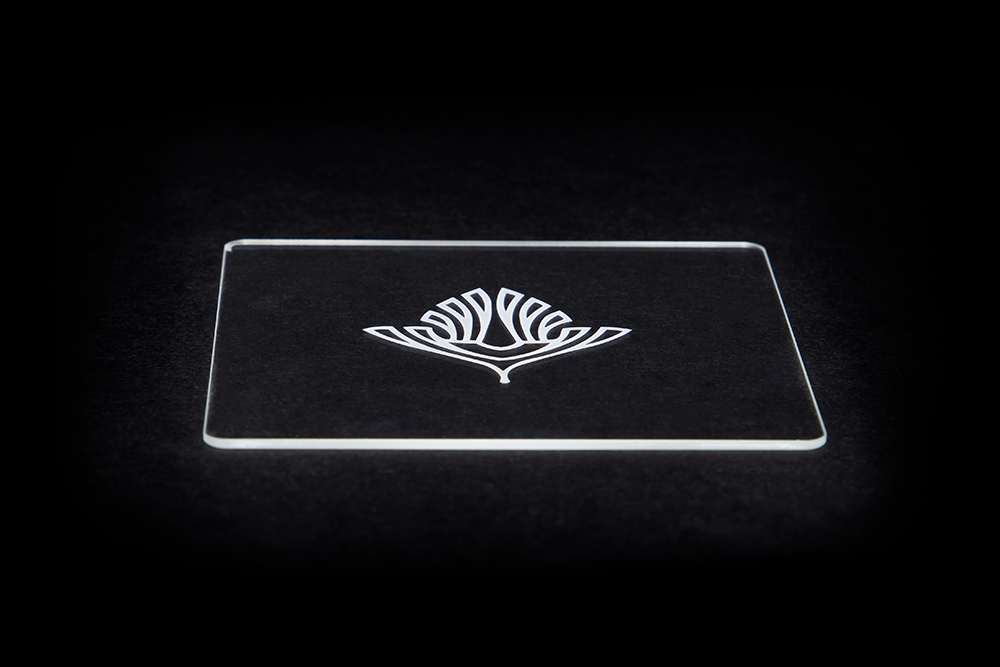
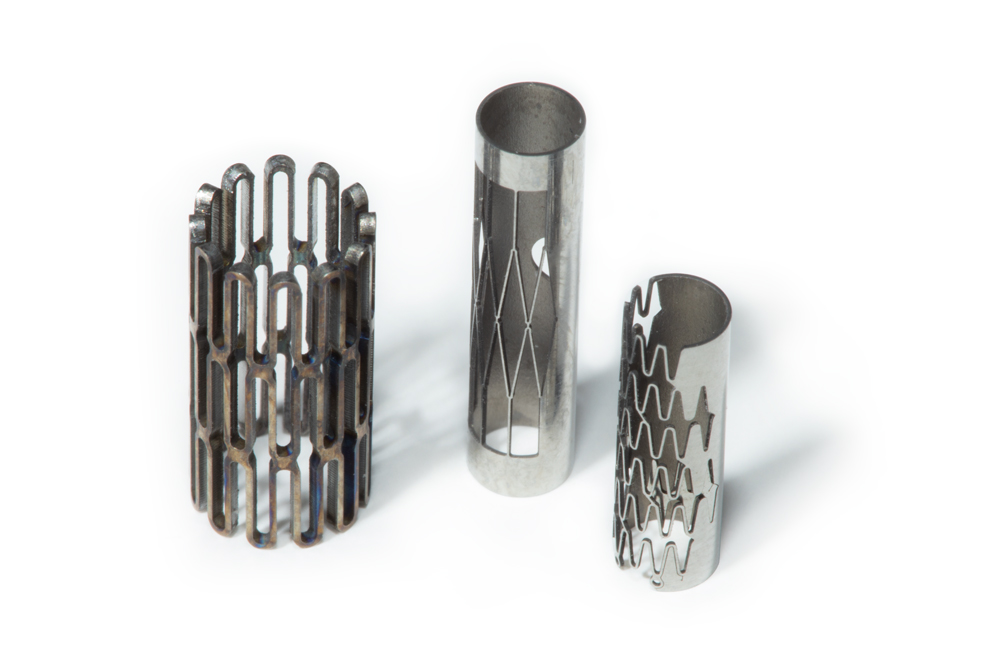
Ultrafast Pulses Eliminate Negative Heat Effects

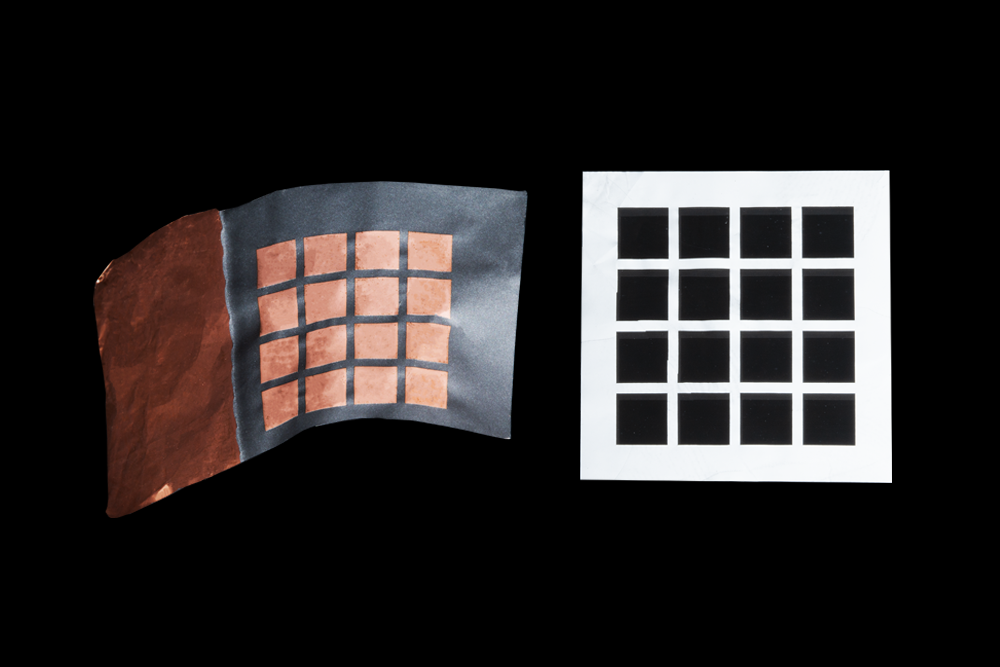
For the purpose of laser-material interaction, the definition of "ultrafast" typically refers to a non-thermal regime of energy absorption. This "cold" processing is a primary distinguishing factor between lasers with picosecond and femtosecond pulse durations and lasers with pulse durations measured in nanoseconds. The non-thermal absorption regime is critically important for some applications because it virtually eliminates thermal damage to materials, enables the creation of smaller features, and allows for more precise control over the process. Two major mechanisms are responsible for the shift from thermal to non-thermal regimes.
High Peak Power: Relative to average output power, ultrafast lasers generate higher peak powers when compared to continuous wave, quasi-continuous wave, and nanosecond lasers. This exceptionally high peak power results in the simultaneous aborption of several photons by the target material. The energy of these photons is additive due to reaching the target at the same time and in the same space.
Cold Ablation: The short pulse duration of ultrafast lasers greatly limits the time available for heat to diffuse into the bulk material. Individual pulses instantly remove or ablate an extremely small volume of material while creating virtually no heat affected zone. Increasing the pulse energy leads to higher material removal rates rather than additional heating.
Ultrafast Laser Applications

Industry Leading Ultrafast Fiber Laser Technology
Taking advantage of unmatched fiber laser expertise, IPG has developed a series of robust, compact, and cost effective ultrafast laser optimized for industrial use. By eliminating cost barriers to ownership and greatly simplifying ease of integration, IPG laser technology allows users at virtually any scale of production to take advantage of the benefits offered by ultrafast lasers.
IPG offers a diverse portfolio of ultrafast laser products across a wide range of parameters. IPG ultrafast lasers are available in wavelengths from deep UV to mid-IR, pulse durations from 250 femtoseconds to 5 picoseconds, and with a variety of average power, pulse energy, and repetition rate options.
Ultrafast Fiber Lasers Across the Spectrum